Light Spectrum Chart Interpretation: A Guide for Indoor Grow Light Projects
Light Spectrum and Plant Growth
The light spectrum significantly affects plant growth, specifically through photosynthesis – the process plants use to convert light energy into chemical energy. Different colors of light, dictated by their varying wavelengths, contribute diverse elements to plant health. Blue light encourages leafy growth and aids in photosynthesis, while red light promotes flowering and fruit production. Green light is majorly reflected back which is why plants appear green. However, it is important to note that plants ideally need a balance of light across the spectrum for optimal growth. Our understanding of how plants use light for photosynthesis has led to the development of specialized, spectrum-tailored LED lights for indoor gardening. Such innovations enhance plant growth by offering a more controlled light environment.
What is the Grow Light Spectrum?
The Grow Light Spectrum refers to the range of light wavelengths that plants receive to carry out photosynthesis, their essential process of converting light into chemical energy. This spectrum is composed of different colors, each with distinct properties and effects on plant growth. The spectrum’s main components are ultraviolet, blue, green, red, and far-red light. Ultraviolet light, while less utilized in photosynthesis, aids in creating stronger, more resistant plants. Blue light is instrumental in regulating plant growth, promoting strong roots, and enhancing overall health. Green light is often overlooked due to its less direct role in photosynthesis but is crucial in penetrating deeper into plant tissues and canopies in combination with blue and red lights. Red light stimulates flowering and fruiting stages, boosting yields. Finally, far-red light signals plants to undergo adaptive changes, like elongation, to compete for orange light and other parts of the full spectrum lighting.
Artificial grow lights aim to mimic this natural light spectrum to optimize indoor plant growth and development. Some lights cover the full spectrum, while others target specific wavelengths to promote certain growth stages or traits. The advances in grow lighting technology, particularly Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs), have made it possible to customize the light spectrum to the specific needs of different plant species. Choosing the right spectrum is pivotal in maximizing the productivity and efficiency of indoor hydroponic or gardening systems. Understanding the Grow Light Spectrum is, thus, vital to nurture plants effectively in controlled environments where natural sunlight isn’t available.
What is a Grow Light Spectrum Chart and why is it important?
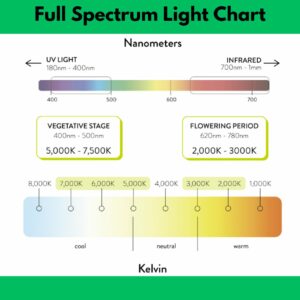
A Grow Light Spectrum Chart is a visual tool used to analyze the light spectrum emitted by grow lights, which are used for indoor or greenhouse horticulture. This chart details the different color wavelengths that the given grow light can produce. Each color corresponds to a specific wavelength measured in nanometers, and certain color wavelengths are more beneficial for plant growth than others. For instance, red and blue light spectrums are crucial for photosynthesis. The importance of this chart lies in optimizing plant health and productivity. Growers use this information to select the most appropriate grow lights, ensuring their plants receive the correct spectrum for specific growth stages and types of plants. Thus, a Grow Light Spectrum Chart is pivotal in indoor gardening or farming scenarios, aiding in the effective nurturing and successful growth of plants.
Defining the Spectrum in Grow Light Spectrum
The Grow Light Spectrum is a critical component in indoor gardening and hydroponics. It refers to the range of light wavelengths that are required for plants to perform photosynthesis effectively. This spectrum includes several segments like ultraviolet (UV) light, visible light, and infrared (IR) light, each providing unique benefits for plant growth. UV light, for instance, promotes plant strength and disease resistance. Visible light, comprised of blue, green, and red light, plays crucial roles in plant development and flowering, while IR light induces flowering and fruiting. Understanding and implementing the right mix of the grow light spectrum can enhance overall plant health and productivity.
Understanding the Importance of Grow Light Spectrum for Plant Growth
The importance of understanding grow light spectrum for plant growth cannot be overstated. Plants predominantly use light from the blue and red parts of the spectrum for photosynthesis, with each part playing a crucial role. Blue light, which has a wavelength of around 400 to 500 nanometers, is responsible for promoting vegetative growth. This includes leaf and stem growth, and helps the plant photosynthesize more efficiently. Conversely, red light, with a wavelength of approximately 600 to 700 nanometers, is responsible for flowering and fruiting, and encouraging a plant to yield more during its fruiting stage. Understanding these aspects can greatly enhance indoor farming and horticulture efforts. By adjusting the color spectrum of the grow light, one can manipulate plant growth stages and boost yields. This increases efficiency and productivity, reducing costs in the long run. Therefore, comprehending the importance of the grow light spectrum stands pivotal to enhancing the success rate of indoor plant growth.
The Role of Different Light Spectrums in Plant Growth
Different light spectrums play a crucial role in plant growth, substantially influencing the photosynthesis process. For example, blue light, which is part of the visible light spectrum, promotes leaf growth by regulating stomatal opening. Red light, on the other hand, is primarily responsible for the plant’s flowering and fruiting stages. Far-red light affects the seed germination process, whereas green light may act as a signaling factor for specific plant responses and can also enhance plant growth when combined with other light spectrums. In actuality, plants use the varying light spectrums to trigger varied biological reactions, thus optimizing their survival and reproduction.
The impact of light on plants is not limited to the visible light spectrum. Ultraviolet (UV) light, which has a shorter wavelength than visible light, can impact plant growth and development. Low levels of UV can stimulate plant growth, while high levels can have harmful consequences, potentially causing damage to plant tissues and impeding growth. Infrared light, which has a longer wavelength than visible light, affects the flowering and budding of plants. For instance, it influences the photoperiodic response of plants –- a biological response to the changing lengths of day and night. This response plays a crucial role in floral initiation, the process by which plants shift from vegetative to reproductive growth.
Moreover, the direction, intensity, and duration of light exposure are also essential factors influencing plant growth and development. Strong light can enhance plant growth and help them produce more nutritious fruit, but too much light can cause photoinhibition and potentially damage plant tissues. The duration of light exposure, or photoperiod, can regulate the flowering in certain plant species, making it an important factor in indoor and greenhouse cultivation. Light duration changes can signal plants to enter different stages, such as vegetative growth or flowering.
The study and application of light spectrum manipulation in plant growth contribute to a variety of fields, including indoor farming, greenhouse management, and plant breeding. By controlling the light spectrum, scientists and farmers can manage plant growth, stimulate specific plant behaviors, and optimize agricultural yields. The precise use of the varying light spectrums holds promise for revolutionizing agricultural practices and the fields of plant physiology and botany.
Visible Light in the Grow Light Spectrum
Visible light plays a crucial role in the grow light spectrum, also known as photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). This spectrum, ranging from 400 to 700 nanometers, encompasses wavelengths that plants specifically absorb and utilize for photosynthesis. Visible light includes blue and red light, which are particularly beneficial for vegetative growth and flowering stages, respectively. Adequate distribution of visible light is, therefore, essential for optimal plant development.
Introduction to Ultraviolet Light in the Spectrum
Ultraviolet (UV) light is a type of electromagnetic radiation that sits within the light spectrum, between visible light and X-rays. With a wavelength shorter than visible light, but longer than X-rays, it is not visible to the human eye. UV light is categorized into three types; UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C. Despite UV light playing a significant role in the production of vitamin D, excessive exposure can be harmful, leading to skin damage and various eye disorders.
How does the LED Grow Light Spectrum differ?
The Light Emitting Diode (LED) grow light spectrum is distinct from traditional horticultural lighting systems. While conventional grow lights emit a full spectrum of light – which includes unnecessary colors like green and yellow – LED grow lights are specifically engineered to output the optimal wavelengths of light most beneficial for plant growth. These wavelengths primarily fall in the red and blue spectrums. Red light is crucially important in the process of plant photosynthesis, promoting flowering and fruiting. Blue light, on the other hand, is necessary for the healthy growth of leaves and stems. Since LED grow lights emit targeted wavelengths, they are more energy-efficient, facilitating the same plant growth while using less electricity. Manufacturers can also customize LED grow lights, allowing specific control over which color wavelengths to emit and in what proportions. This level of precision enables growers to tailor their lighting system according to the specific needs of their plants, thereby optimizing plant health and productivity.
Advantages and Special Features of LED Grow Lights
LED Grow Lights, produced by a light source, offer multiple advantages and special features like providing the ideal spectrum that sets them apart from traditional lighting systems. One of the major benefits is energy efficiency; they consume less power, saving up to 70% on energy costs. They ensure optimal plant growth by providing a tailored light spectrum suitable for photosynthesis. Additionally, LED grow lights have a longer lifespan – typically 50,000 to 100,000 hours. They also operate at much cooler temperatures, thereby reducing the risk of plant damage. Notably, they are more environmentally friendly, as they contain no toxic materials and are 100% recyclable. Their compact size and flexibility also offer the user a significant degree of positioning freedom.
LED Grow Light Spectrum Vs Traditional Light Source Spectrum
LED grow lights provide a spectrum of light that is specifically designed to support plant growth. Compared to the traditional light source spectrum, LED grow lights offer a broader range of wavelengths, making them more beneficial for various stages of plant growth. LED lights can provide specific light spectrums such as orange light, to enhance photosynthesis and plant flowering, promoting overall healthier growth. Traditional light sources, on the other hand, give off a fixed spectrum of light that cannot be adjusted to suit different plant needs. Additionally, LED grow lights consume less energy and have a longer lifespan, making them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly than traditional light sources.
Red and Blue Light in LED Grow Light Spectrum
The LED Grow Light Spectrum is a revolutionary way to promote plant growth and yield. It employs the use of both red and blue light, offering a diverse light spectrum conducive to plant photosynthesis. Red light, usually in the range of 620-760nm, encourages flowering and fruit production. In contrast, blue light, generally between 430-470nm, fosters the vegetative growth, promoting leaf and stem development. The balanced utilization of both red and blue light in LED Grow Light Spectrum aims to mimic the sunlight’s natural qualities, providing an optimized environment for indoor plants to flourish. Thus, LED Grow Light Spectrum’s integration of these light waves is transforming indoor gardening practices.
Insights on Full Spectrum LED Grow Lights
Full Spectrum LED Grow Lights operate by delivering a full spectrum of light, mimicking natural sunlight, to facilitate growth in plants. These innovative lights are known for their efficiency and durability, offering significant energy savings compared to traditional grow lights. Full Spectrum LED lights cover all stages of plant growth, from germination to flowering, and are suitable for all types of indoor plants and hydroponics. They are designed with a balanced light spectrum, which ensures the health of plants by stimulating photosynthesis and promoting optimal growth and development. Therefore, Full Spectrum LED Grow Lights offer a versatile and effective solution for indoor gardening enthusiasts, improving productivity and plant health.
The Ideal LED Grow Light Spectrum
The ideal LED grow light spectrum significantly impacts the potency, quality, and yield of plant growth. This spectrum provides the essential wavelengths of light that specifically cater to photosynthesis. It typically ranges from 400 to 700 nanometers, encompassing blue (vegging stage) and red (flowering stage) lights primarily. However, other colors like UV, IR, and white also contribute to well-rounded plant growth. High-quality LED grow lights offer a full spectrum, ensuring plants receive the right type of light at the right stage. With the proper spectrum, LED grow lights can effectively mimic the sun, enabling indoor growers to cultivate healthy and productive plants all year round.
How can Growers use the Grow Light Spectrum Chart effectively?
Growers can use the Grow Light Spectrum Chart effectively to optimize the growth and health of their plants. This chart visually illustrates the different wavelengths of light that plants need at various stages of growth, namely, germination, vegetative growth, and flowering. By understanding and applying the information on a Grow Light Spectrum Chart, the growers can choose the right types of grow lights that emit the specific light spectrums required for each stage. For example, blue light, usually strong during spring, is ideal for leaf growth during the vegetative stage, while red light, which is abundant during summer and fall, encourages blooming during the flowering stage. It is also essential to consider the intensity and duration of light exposure, as these factors can significantly impact plant growth and yield. Thus, using a Grow Light Spectrum Chart can assist growers in making informed lighting decisions, leading to efficient indoor farming or controlled environment agriculture.
Using the Grow Light Spectrum Chart for Different Plant Species
The Grow Light Spectrum Chart is a valuable tool for gardeners and cultivators as it serves as a guide to the specific light spectrums needed by different plant species. This chart effectively helps in understanding the essential light requirements for the photosynthesis process in plants. It provides detailed information on the ideal light spectrum, ranging from UV to far-red light, required for optimal growth and health of various plant species. By utilizing this chart, indoor growers can ensure their plants receive the correct type and amount of light necessary for healthy development. The ability to cater to the unique light requirements of different plants dramatically enhances their rate of growth, making the Grow Light Spectrum Chart an indispensable asset for indoor gardening.
Choosing the Right Light Spectrum for Your Indoor Plants
Choosing the right light spectrum for your indoor plants is critical for their survival and growth. Indoor plants use light, specifically spectrum light, to photosynthesize and produce their food, and different light spectra, measured in nm, influence this process crucially. Blue light is beneficial for promoting vegetative growth, while red light is essential for blooming and fruiting. Full-spectrum lights, mimicking the natural sunlight, can be the best solution, providing all the light colors your plants may need. Look out for LED grow lights, particularly advantageous because they’re energy-efficient and can be tuned to emit specific colors from the light spectrum. Ultimately, understanding your plants’ lighting needs can make a significant difference in their health and development.
Expert Tips on Using LED Grow Lights Effectively
Expert tips on using LED grow lights effectively can significantly enhance your indoor gardening experience. Firstly, maintain an optimal distance between your plants and the LED lights; this varies according to the plant species and the light intensity. Secondly, growers use a timer to regulate the on-off light cycles, imitating the natural sunlight patterns to maximize the photosynthetic activity of the plants, thereby enhancing their growth patterns. Thirdly, adjust the color spectrum of your LED lights according to the specific growth phase of the plant, as different wavelengths stimulate various stages of the plant’s life cycle. Lastly, consider the energy consumption and make sure your LED grow lights are energy-efficient, which not only improves plant growth but also reduces utility costs.
Importance of Specific Light Wavelengths for Different Grow Phases
Light wavelengths play a vital role in the development of plants in different growth phases. For seed germination and initial growth, plants absorb blue light (around 400-500nm wavelength) to boost vegetative growth of leaves and stems. As they approach the flowering and fruiting stage, plants require more red light (around 600-700nm wavelength), aiding in photosynthesis and driving their maturation. Certain crops even utilize far-red light (700-750nm) to regulate shade avoidance responses and flowering time. Hence, by manipulating the light spectrum, farmers and researchers can guide the growth, yield, and quality of crops, making the understanding and application of specific light wavelengths crucial in modern agriculture.
Understanding Short-Day Plants and Light Spectrum
Short-day plants are unique in their growth patterns, particularly regarding their response to light spectrum and day length. These plants predominantly flower when the daylight period is less than a specific duration, usually around twelve hours. Plants respond to light based on a photoperiod mechanism that involves the plant’s recognition of the light spectrum, particularly red and far-red light, for chlorophyll absorption. By detecting the ratio between red and far-red light, short-day plants ascertain whether the sun is setting or not. Understanding this incredible mechanism not only provides insight into the adaptive strategies of these plants but can also contribute significantly to improving agricultural productivity by making farmers more equipped in adjusting light periods and wavelengths, to optimally nurture these crops.
Final Thoughts on LED Light Spectrum Considerations
After extensive review and understanding of LED light spectrum considerations, it can be concluded that the choice of LED light largely depends on the specific application and requirements. Whether it’s for promoting plant growth in horticulture, creating mood lighting in a residential setting, or ensuring visibility in industrial applications, the LED light spectrum plays a pivotal role. The blue-to-red ratio, CRI, and color temperature are crucial parameters that determine the effectiveness of LED lights in different applications. The benefit of energy efficiency and long lifespan further add to the appeal of LED lights. While selecting LED lights, balancing between these spectrum considerations ensures optimum performance. In conclusion, a deep understanding of the LED light spectrum is indispensable in making informed decisions and achieving desired results.
